In computer networking, Port forwarding or Port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway (external network), by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.
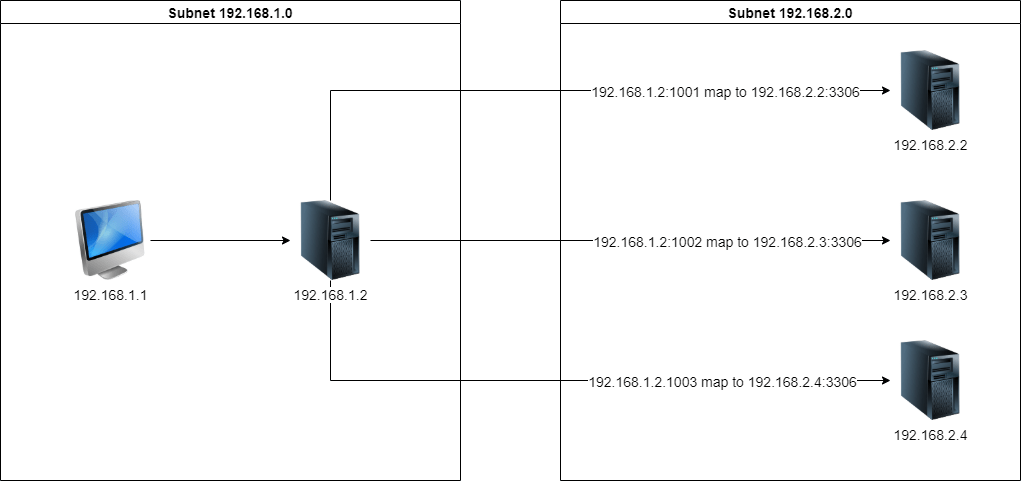
The client side is not allowed to access subnet 192.168.2.0 directly but server 192.168.1.2 can help to redirect the TCP request to the subnet 192.168.2.0. It can also prevent to expose the subnet IP to the public.
Implementation
We are going to build a tunnel by two threads on the script. One of threads is a socket client and another one is socket server. What we are going to do is connect both of them together and the packet stream can be streaming here.
The libraries we need to import:
import time
import socket
import _thread
import sys
import getopt
How to run the script
def exception():
print('Usage : port_forward.py -f -i -p ')
def main(argv):
from_port = 0
ip = ''
to_port = 0
try:
opts, args = getopt.getopt(
argv, "h:f:i:t:", ["help", "from_port=", "ip=", "to_port="])
if len(opts) != 3:
exception()
for opt, arg in opts:
if opt in ("-h", "--help"):
exception()
elif opt in ("-f", "--from_port"):
from_port = int(arg)
elif opt in ("-i", "--ip"):
ip = arg
elif opt in ("-t", "--to_port"):
to_port = int(arg)
except getopt.GetoptError:
exception()
tunnel(from_port, ip, to_port)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv[1:])
> python3 port_forward.py -f (from port) -i (ip) -p (to port)
For example of localhost:8089 mapping to localhost:8081
tunnel(8089, '127.0.0.1', 8081)
Build and connect the socket tunnel between host and destination by two threads.
# Buffer size
buffer = 2048
# Maximum connections
backlog = 10
localhost = '127.0.0.1'
def tunnel(from_port, to_ip, to_port, local_ip=''):
global backlog
if local_ip is '' or local_ip is None:
local_ip = localhost
if to_ip is '' or to_ip is None:
to_ip = localhost
print("Listening from {} to {}".format(
full_address(local_ip, from_port), full_address(to_ip, to_port)))
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.bind((local_ip, from_port))
sock.listen(backlog)
while True:
sock, address = sock.accept()
print("Connected from local port{} to destination {}".format(
from_port, address[0]))
forward = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
forward.connect((to_ip, to_port))
build_tunnel(sock, forward)
except Exception as ex:
print("Connection Error {}, retry after 5 seconds ".format(ex))
time.sleep(5)
tunnel(from_port, to_ip, to_port, local_ip)
def build_tunnel(socket, forward):
try:
_thread.start_new_thread(socket_pipeline, (socket, forward))
_thread.start_new_thread(socket_pipeline, (forward, socket))
except Exception as e:
print("error {}".format(e))
raise e
while True:
pass
def socket_pipeline(source, sink):
print("Socket pipeline created from {} to {}".format(
source.getpeername(), sink.getpeername()))
global buffer
while True:
try:
data = source.recv(buffer)
if not data:
break
sink.send(data)
except Exception as ex:
print("error {}".format(ex))
raise ex
source.close()
sink.close()
